HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language. It is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
It defines the structure or outline of the webpage content.
Websites are displayed on browsers, and HTML elements guide the browser on how to display the webpage content.
Coding in HTML
We can just simply type our text into an HTML file, but it is very important to specify the type of text to the browser, hence we use tags.
There are two main tags in HTML
Head Tag
Body tag
The head tag contains the title and logo of the webpage and is displayed on the navigation bar
The body tag contains all the information of the website.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
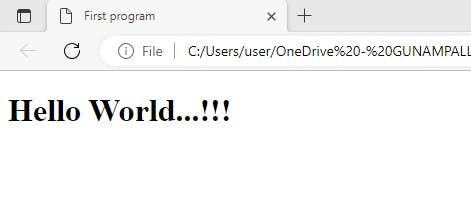
<title>First program</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World...!!!</h1>
</body>
</html>
Comments
HTML comments are a way to add notes and explanations to your HTML code without them being visible to users when the page is rendered in a web browser. They are used to provide context and documentation for the code and can be useful for commenting out parts of your code that you want to temporarily disable without removing them entirely.
You can add comments to your HTML code by enclosing them within the <!---and----> tags
<body>
<!-- heading -->
<h1>Hello World...!!!</h1>
</body>
Tags
In HTML, tags are used to define the structure and layout of a webpage. They are the basic building blocks that are used to create elements on a page. For example, the <p> tag is used to create a paragraph element, while the <h1> tag is used to create a heading element. The tag may appear in pairs, with an opening tag and a closing tag, like this:<tag> Content </tag> or sometimes self-closing like:<tag/>.
Element
Elements are the individual components of an HTML document, such as headings, paragraphs, and images. Each element is represented by a corresponding HTML tag. For example, a paragraph element is represented by the <p> tag, and a heading element is represented by the <h1>,<h2>, etc. tags. The element content is the content between the opening and closing tags.
Attributes
Attributes are used to provide additional information about an element. They are added to the opening tag of an element, and they always come in the form of name-value pairs. For example, the src attribute is used to specify the source of an image, and the href attribute is used to specify the destination of a link.
