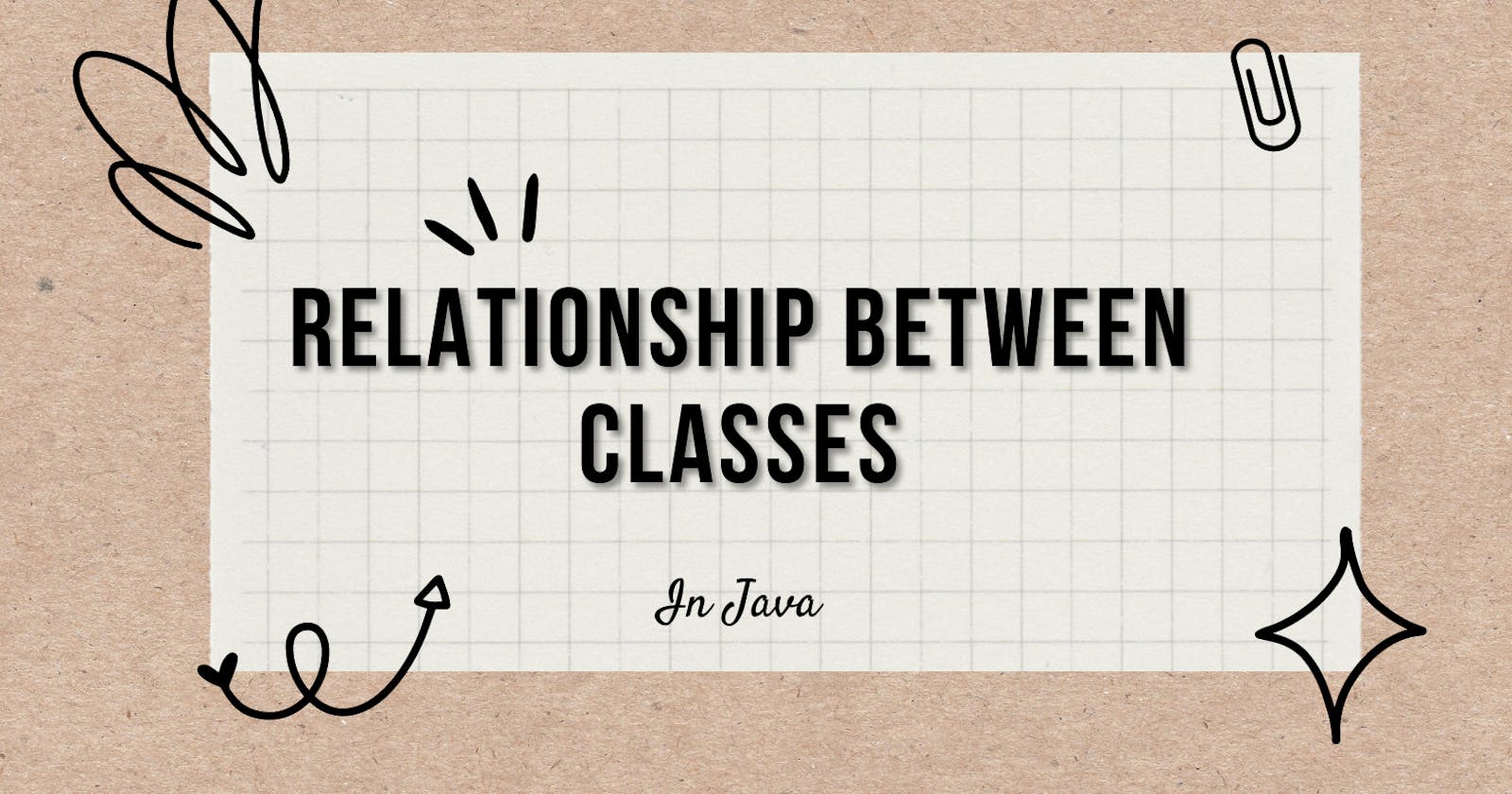
There are mainly two types of relationships between classes in JAVA
Inheritance (IS-A)
Association (HAS-A)
Inheritance
In inheritance, the child class object carries the body of the parent class when initiated. This is achieved using the "extends" keyword.
class Vehicle
{
}
class car extends Vehicle
{
}
Association
Association is the relation between two separate classes established through objects. There are two forms of association
Aggregation
Composition
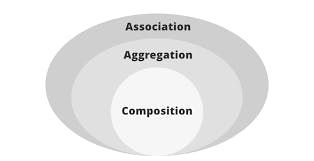
In Aggregation, both entries can survive individually, which means ending one entity will not affect the other.
For example, consider a car having a music player and an engine. The music player can work even without a car; this indicates aggregation, whereas an engine cannot work without a car this is an example of composition.
class Vehicle
{
}
class car
{
Engine e=new Engine();
}
Advantages
Code reusability
Cost cutting
Reduce redundancy